ESPE2015 Poster Category 3 Turner (14 abstracts)
Growth Characteristics of Patient with Turner Syndrome Different Age and Karyotypes by the Ukrainian National Register
Nataliya Zelinska a , Irina Shevchenko a , Evgenia Globa a & Nataliya Pogadaeva b
aUkrainian Scientific and Practical Center of Endocrine Surgery, Transplantation of Endocrine Organs and Tissues of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine, Kiev, Ukraine; bNation Children’s Specialized Hospital ‘Okhmatdet’, Kiev, Ukraine
Background: Turner syndrome (TS) is the most well-known and common chromosomal disorder accompanied by delayed growth. According to the Ukrainian national register (UNR) of children with dwarfism the growth retardation is common for all girls with TS.
Objective and hypotheses: The aim of the study was to determine the growth parameters of TS girls different age and karyotype, before GH treatment.
Method: According to the UNR it was provided a retrospective analysis in 2005–2014 years of growth parameters at 502 girls with TS aged 1–17 years old before GH treatment.
Results: Growth delay in untreated girls with TS progresses with age: from −1.6±1.3 S.D. (children aged 1 years old) to −3.5±1.2 S.D. (age >17 years old). There was no significant difference in growth in TS girls with different karyotype (monosomy X, mosaicism and structural abnormalities of chromosome X) (P(0.05). Average height in patients with 45,X was 126.7±18.5 cm (−3.2±1.1 S.D.), with mosaicism −127.7±17.8 cm (−2.8±1.1 S.D.), with structural anomalies chromosome X −125.5±17.0 cm (−3.3±0.9 S.D.).
Conclusion: There is no difference in degree of growth retardation at TS girls with different karyotype. Growth delayed in TS girls is noticeable from the first year of life, increases with age, and is a greatest in the pubertal age. The mean growth delay in TS girls is −3.1±1.1 S.D. and is greatest in the age of 14 years.
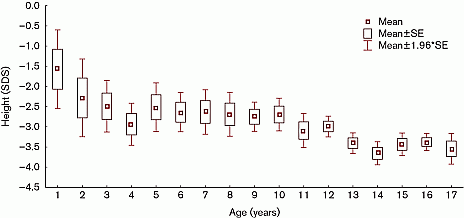
Figure 1 Degree of growth retardation at girls with TS.
 }
}



